Acne Scarring
Causes, Treatment, Prevention
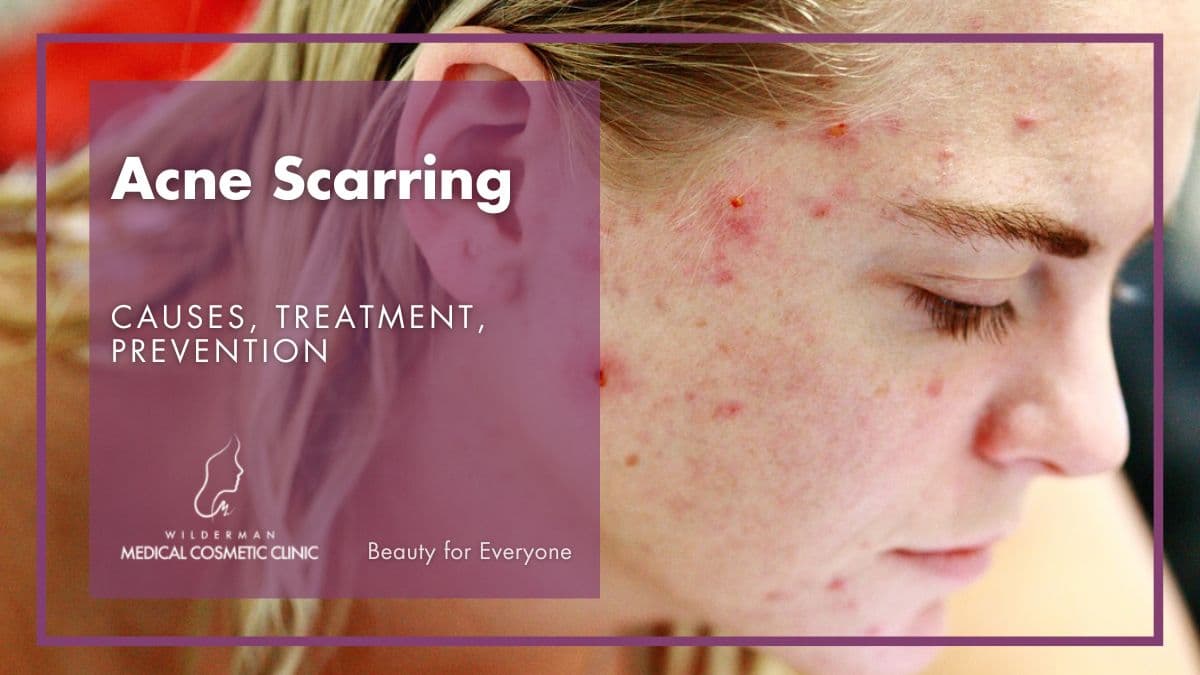
Acne is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide, causing physical and emotional distress.
In some cases, acne can leave behind unsightly scars, further impacting one’s self-esteem.
Get immediate answers about possible treatment options tailored for you, expected results, and much more.
- Expert Diagnosis
- Customized Treatment Plans
- No Obligation
- Comfort and Privacy
- Immediate Answers
Understanding the causes, types, and treatment options for acne scarring can help individuals effectively manage and minimize the long-term effects of this condition.
What causes acne?
Acne occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria.
Several factors contribute to the development of acne, including:
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations in hormones, especially during puberty, can trigger acne by increasing oil production and clogging hair follicles.
- Excess sebum production: Overactive sebaceous glands can lead to oily skin, which is more prone to acne breakouts.
- Bacteria: Propionibacterium acnes ( acnes) bacteria thrive in the presence of excess sebum and dead skin cells, causing inflammation and infection that contribute to acne formation.
- Follicular hyperkeratinization: Abnormal shedding of cells in hair follicles results in clumping and blockages, leading to the formation of non-inflammatory acne-like whiteheads and blackheads.
- Inflammation: When bacteria and the immune system interact in hair follicles, it causes inflammation, redness, swelling, and the formation of inflammatory acne lesions.
- Genetic factors: Family history can increase the likelihood of developing acne if there is a history of acne in your parents or close relatives.
- Lifestyle factors: Diet (high glycemic index foods and dairy products, in particular), stress, certain medications, and comedogenic cosmetics or skincare products can contribute to acne breakouts.
It is important to note that acne causes can vary from person to person, and a combination of factors often contributes to its development.
What are the different types of acne?
There are several types of acne, each characterized by different symptoms and appearances. The common types of acne include:
- Whiteheads: Small, closed bumps on the skin’s surface caused by hair follicles clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria.
- Blackheads: Open comedones with a dark appearance due to oxidation of sebum and dead skin cells, often seen as small dark spots on the skin.
- Papules: Small, raised, red bumps caused by inflammation when hair follicle walls break, resulting in an immune response and resulting swelling.
- Pustules: Red bumps with a white or yellow center, containing pus. They are similar to papules but have visible pus.
- Nodules: Large, solid, painful lumps that develop beneath the skin’s surface due to a buildup of bacteria, oil, and dead skin cells deep within the hair follicles.
- Cysts: Deep, painful, pus-filled lesions that are larger and more severe than pustules. They occur when infection and inflammation spread deep into the skin, often leading to scarring and requiring medical intervention.
It is important to note that acne can present as a combination of these different types, and the severity of acne can vary from person to person.
How does acne cause scars?
Acne can cause scarring due to the inflammatory response and damage to the skin’s tissues. When acne lesions, such as papules, pustules, nodules, or cysts, are present, the skin undergoes a series of events that can lead to scarring:
- Inflammation: Inflammatory acne lesions cause an immune response in the body, resulting in inflammation. The body releases inflammatory molecules and immune cells to fight off the infection and heal the affected area. However, the inflammatory response can damage the surrounding healthy skin tissues.
- Tissue Damage: Severe acne lesions, such as nodules or cysts, can cause significant damage to the deeper layers of the skin. The inflammation, combined with the accumulation of pus and bacteria, can result in the destruction of collagen and elastin fibers, which are vital for maintaining the skin’s structure and elasticity.
- Delayed Healing: Acne lesions that are deep or take a long time to heal are more likely to result in scarring. Delayed healing can occur due to persistent inflammation, inadequate treatment, or picking or squeezing the acne lesions, which further damages the skin.
- Abnormal Collagen Production: During the healing process, the body produces new collagen fibers to repair the damaged skin. In some cases, collagen production may be irregular, leading to the formation of raised scars (hypertrophic or keloid scars) or depressed scars (atrophic scars).
The type of acne scarring can vary based on the individual’s skin type, the severity of acne, and the body’s healing response. Common types of acne scars include:
- Atrophic scars: They are characterized by depressions or indentations in the skin. There are different subtypes of atrophic scars:
- Ice Pick Scars: Deep, narrow scars that extend into the skin, resembling small holes or pits.
- Boxcar Scars: Broad, rectangular-shaped scars with well-defined edges and a depressed appearance.
- Rolling Scars: Scars that give the skin a wavy or uneven texture.
- Hypertrophic Scars: Raised, thickened scars that may be red or pink and remain within the boundaries of the original acne lesion.
- Keloid Scars: Raised scars that extend beyond the borders of the original acne lesion and can be larger and more prominent.
How common is acne scarring?
Acne scarring is a relatively common occurrence, with studies estimating that around 80% of people who experience acne will develop some form of scarring (Jacob et al., 2001).
The severity of scarring can vary greatly, ranging from mild to severe, and not all individuals with acne will develop noticeable or permanent scars. Factors such as the type and duration of acne, individual skin characteristics, and treatment methods can influence the likelihood and extent of scarring.
Early and effective acne treatment can help reduce the risk of scarring and minimize its appearance.
How are acne scars treated?
Acne scars can be treated through various approaches depending on the type and severity of the scars. Here are some common treatment options:
- Topical Treatments: Certain topical creams or gels containing ingredients like retinoids, alpha hydroxy acids (AHAs), or vitamin C can help improve the appearance of acne scars over time. These products promote skin cell turnover, reduce discoloration, and stimulate collagen production.
- Dermabrasion: Dermabrasion involves the removal of the top layer of the skin using a rotating brush or a diamond wheel. This procedure helps smooth the skin’s surface and reduce the appearance of shallow acne scars. It requires professional expertise and may have some downtime for the skin to heal following a treatment.
- Microdermabrasion: Microdermabrasion is a milder form of dermabrasion that exfoliates the skin using tiny crystals or a diamond-tipped wand. It helps remove dead skin cells and promotes skin renewal. While it may not be as effective for deep scars, it can improve the appearance of mild acne scars and provide a more even skin tone.
- Chemical Peels: Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which causes exfoliation and the removal of the top layers. This helps improve the texture and appearance of acne scars. Superficial peels are effective for mild scars, while deeper peels may be necessary for more severe scars. Multiple sessions may be required for optimal results.
- Radiofrequency (RF): Radiofrequency (RF) treatment involves the use of RF energy to heat the deeper layers of the skin, promoting collagen production and remodeling. This helps to tighten the skin and reduce the visibility of acne scars. RF treatment can be effective for various types of acne scarring, including atrophic scars. It is a safe procedure with minimal discomfort and downtime.
- Microneedling: Microneedling involves using a device with tiny needles to create controlled micro-injuries in the skin. This stimulates collagen production and promotes skin remodeling, leading to the improvement of acne scars. Microneedling can be combined with the application of topical serums or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for enhanced results.
- Morpheus8: Morpheus8 combines microneedling with radiofrequency (RF) energy to improve the appearance of scars and promote skin rejuvenation. During the procedure, tiny needles are inserted into the skin, delivering RF energy to the deeper layers. This stimulates collagen production, tightens the skin, and reduces the appearance of acne scars. Morpheus8 can be effective for various types of acne scarring, and it offers the advantage of minimal downtime and quick recovery.
- Dermal Fillers: Injectable dermal fillers can be used to plump up depressed acne scars, giving them a smoother appearance. The fillers are injected beneath the scar to raise the skin’s surface temporarily. Results are immediate but temporary, usually lasting several months to a year.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments use focused light energy to target and stimulate collagen production in the skin. Different types of lasers, such as fractional lasers or ablative lasers, can be used to treat acne scars. Laser therapy helps resurface the skin, reduce scar depth, and improve overall skin texture. It may require multiple sessions and downtime for skin healing.
- Surgical Procedures: In cases of severe acne scarring, surgical procedures like punch excision, subcision, or skin grafting may be recommended. These procedures aim to physically remove or rearrange scar tissue to improve the skin’s appearance.
The treatment of acne scars varies based on the severity of the scarring. For mild scarring, topical treatments with ingredients like retinoids, AHAs, or vitamin C, as well as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and microneedling, can be effective.
Severe scarring may require laser therapy, dermal fillers, or surgical procedures like punch excision or skin grafting. Combination treatments may also be recommended for optimal results.
Acne scars of different types require specific treatment approaches. For atrophic scars, ice-pick scars may benefit from punch excision or grafting, boxcar scars from laser resurfacing or dermal fillers, and rolling scars from subcision or microneedling. Hypertrophic and keloid scars can be treated with corticosteroid injections, silicone sheets or gel, laser therapy, or cryotherapy.
Pigmented scars may respond to topical creams, chemical peels, or laser treatments. Combination scars may necessitate a tailored combination of treatments like laser therapy, microneedling, subcision, dermal fillers, or surgical techniques.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of each treatment option can vary depending on the individual’s specific scar type, skin condition, and response to treatment.
Consulting with a dermatologist or a skincare professional is crucial to determine the most suitable treatment plan tailored to one’s needs.
Additionally, maintaining a consistent skincare routine, protecting the skin from sun exposure, and managing acne breakouts can help prevent further scarring and support the healing process.
Acne prevention
Here are some tips for acne prevention:
• Cleanse your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser.
• Avoid touching your face and refrain from picking at or popping pimples.
• Use non-comedogenic and oil-free skincare products.
• Moisturize with oil-free or lightweight moisturizers.
• Maintain a balanced diet, avoiding high glycemic index foods and dairy products if they worsen your acne.
• Manage stress through exercise, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
• Keep hair and hair products away from your face.
• Protect your skin from the sun with broad-spectrum sunscreen, protective clothing, and seeking shade.
• Exfoliate gently 1-2 times per week.
• Consult a dermatologist or skincare professional for persistent or severe acne that doesn’t respond to over-the-counter treatments.
Conclusion
Acne scarring can be a distressing consequence of persistent or severe acne. Understanding the causes, types, and treatment options for acne scarring is crucial for effective management.
With advancements in medical and cosmetic procedures, individuals can find relief and restore their confidence by exploring various treatment modalities.
Remember, prevention is key, and adopting a consistent skincare routine and healthy lifestyle habits can go a long way in preventing acne breakouts and maintaining clear, healthy skin.
Reference
Jacob CI, Dover JS, Kaminer MS. Acne scarring: a classification system and review of treatment options. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;45:109–117.
Connolly D, Vu HL, Mariwalla K, Saedi N. Acne Scarring-Pathogenesis, Evaluation, and Treatment Options. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2017 Sep;10(9):12-23. Epub 2017 Sep 1. PMID: 29344322; PMCID: PMC5749614.
Healthline. Acne Scars: Types, Causes, and Treatments. Retrieved from https://www.healthline.com/health/acne-scars#depressed-scars. Accessed on May 30, 2023.
Cleveland Clinic. Acne Scars. Retrieved from https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21222-acne-scars. Accessed on May 30, 2023.
American Academy of Dermatology Association. Acne Scars: Treatment. Retrieved from https://www.aad.org/public/diseases/acne/derm-treat/scars/treatment. Accessed on May 30, 2023.
Other skin conditions that may be of interest
Skin Laxity: A common skin concern – Skin laxity is a common concern that many individuals experience as they age. It is characterized by a loss of firmness, elasticity, and resilience in the skin, leading to a less …
Sagging Skin – As we age, one of the most common concerns we face is sagging skin. The loss of elasticity and firmness can affect various parts of our body, including the face, neck, arms, and abdomen. Sagging skin can be attributed to …
Stretch Marks: Causes, Treatments, Prevention – Stretch marks, also known as striae, are a common skin condition that affects both men and women. They often appear as visible lines on the skin, typically on …
Spider Veins and Broken Capillaries – Spider veins and broken capillaries are common vascular conditions that affect a significant number of people. While they are typically harmless, they can cause cosmetic concerns for …
Oily Skin – Oily skin is a common dermatological condition characterized by excess sebum production, which can lead to a shiny, greasy appearance and potential skin issues such as acne breakouts and clogged pores. While it can be …
Smoker’s lines: A real connection to smoking? – Smoker’s lines, also known as lip lines, lipstick lines, or perioral wrinkles, are fine lines that develop around the mouth and lips. These lines can be unsightly and may contribute to …
Skin Redness and Inflammation: Causes, Diagnosis, Treatments, Tips – Skin inflammation is caused by the body’s response to an irritant, injury, infection, or immune system dysfunction that affects the skin. It is characterized by …
Dark Under-Eye Circles – Dark under-eye circles can be frustrating and make you appear tired or older than you actually are. They are a common cosmetic concern that affects people of all ages. We will explore what …
Stay Ahead of the Beauty Curve
Beyond Beauty: Elevate Your Routine with Insider Tips and Breakthroughs – Subscribe Now!
Transform your beauty routine into something extraordinary!


